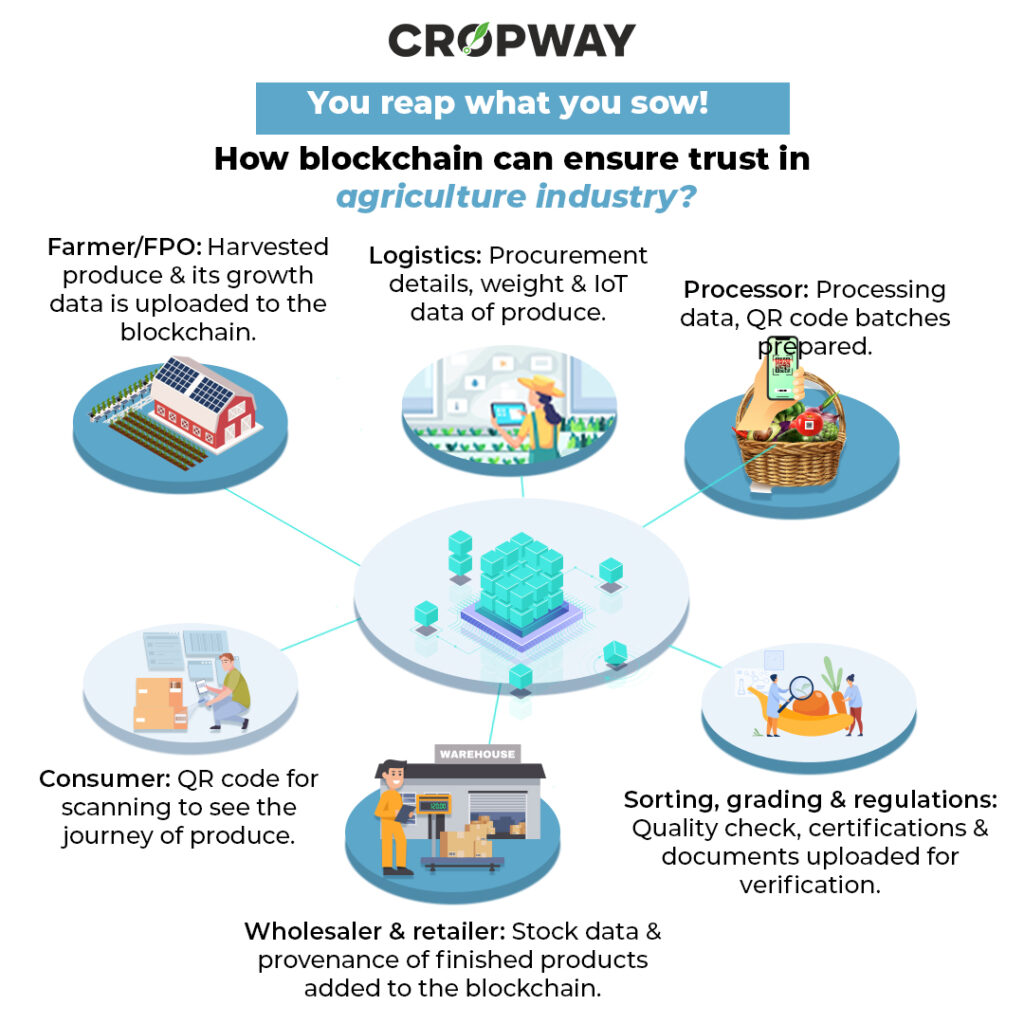
How blockchain can ensure trust in agriculture industry?
The food industry is currently undergoing tremendous changes due to the rise of online shopping and the increase in demand for convenience foods. In order to ensure consumer safety, retailers have been implementing various methods to track their products throughout the supply chain. However, these methods are not without flaws. One of the biggest problems is that they require manual intervention and rely heavily on trust between parties. These systems do not provide real-time information about where a product came from or how long it spent at each stage of production.
Ensuring food traceability using blockchain
The difficulty in determining the origin of any produce is primarily due to the global supply chain’s size and complexity. The crop passes through several supply chain stages before reaching the consumer, including farming cooperatives, exporters, graders, shippers, manufacturers, and so on.
Blockchain can record immutable information at every stage of the food supply chain, it can provide reliable data about the provenance of food items and the precise journey they took from farm to fork. With a single screen tap, customers could learn which certified farm their mangoes were picked from or which sea their fish was caught in.
So, what is blockchain?
Blockchain is fundamentally an electronic system that enables the real-time recording of transactions. A blockchain system keeps track of the time, date, type, and cost of each transaction that users complete. The information is then securely and immutably recorded and may be made available to every other participant in the system after the parties have agreed that it is accurate. So, using blockchain technology, a “consolidated record that comprises a single and shared version of the truth” is instantly created.
Benefits of blockchain in agriculture industry
There are several difficulties that can be addressed with the use of this technology. As Blockchain has the power to give a customisable suite of solutions that promise to enhance food safety and freshness, restore supply chain efficiency, decrease waste, increase the retailer’s brand’s image in the chain, and directly support stakeholders at the bottom of the pyramid.
While employing technology alone to prohibit unethical supply chain activities or inefficiencies may sound overly idealistic, many of the ingredients are already in place to make it a reality. Connecting the links might result in global social transformation, given that supply chain digitization, farm-to-shelf food traceability, and identity partnerships are already using blockchain to disrupt their respective industries.
You might also want to read:https://www.cropway.com/blockchain-in-agriculture/
Over the past 30 years, there have been countless technical advances, but none of them have been able to resolve the trust issue. However, with the introduction of blockchain, we can now start to address these issues; all that is left to do is connect the dots.