What Exactly Is Carbon Footprint?
The amount of greenhouse gases discharged into the atmosphere as a whole is measured by the term “carbon footprint.”
These emissions are the result of decisions and actions made directly or indirectly by a person, a business, or a nation. The carbon footprint is estimated in terms of carbon dioxide emissions (CO2).

What Causes Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions?
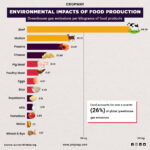
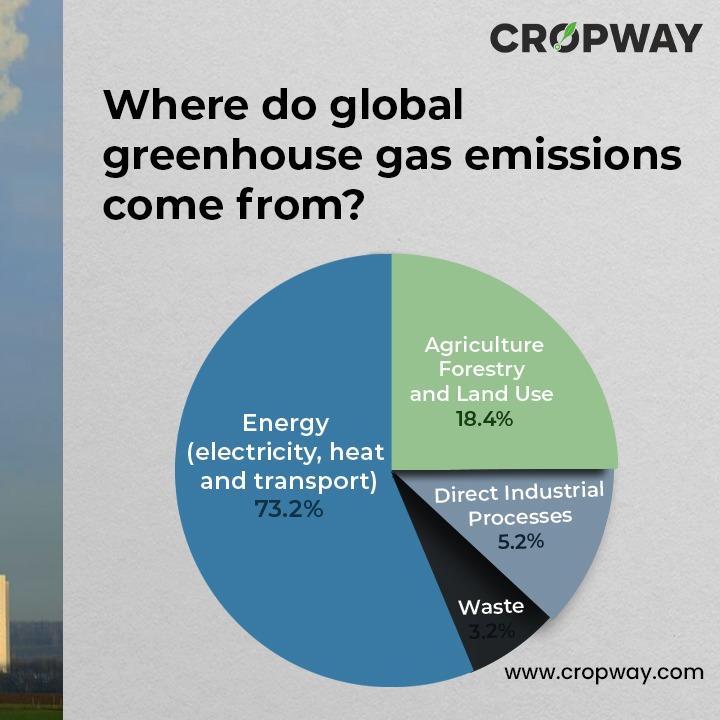
Emissions from agriculture make up a sizable share of all world emissions. When we look at this over a 20-year period, agriculture contributes to around 20% of world GHG emissions, wherein forestry contributes to about 7%, and land use change contributes to about 2%. As a source of emissions, agriculture is thus virtually as significant as industry.
- Energy (electricity, heat and transport): 73.2%
- Direct Industrial Processes: 5.2%
- Waste: 3.2%
- Agriculture, Forestry and Land Use: 18.4%
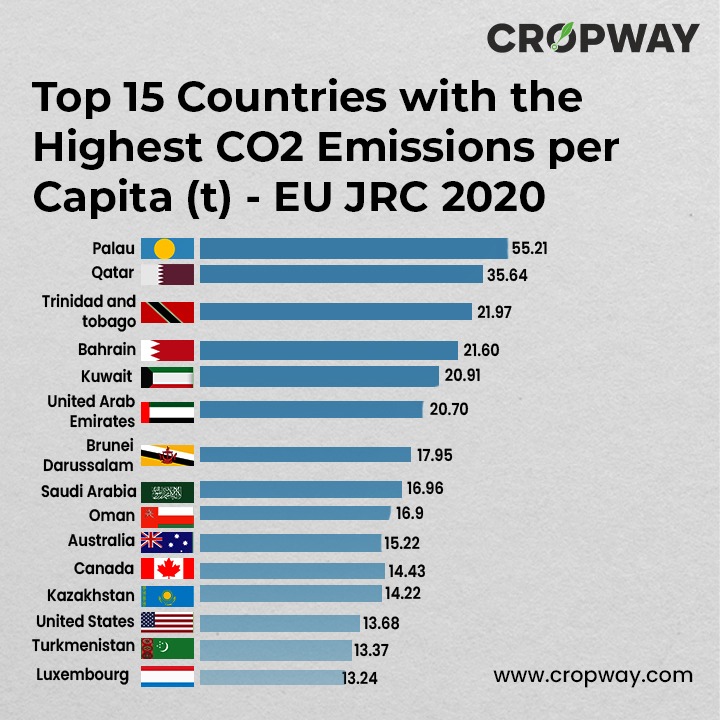
Top 15 Countries with the Highest CO2 Emissions per Capita (t) – EU JRC 2020
- Palau — 55.29
- Qatar — 35.64
- Trinidad and Tobago — 21.97
- Bahrain — 21.60
- Kuwait — 20.91
- United Arab Emirates — 20.70
- Brunei Darussalam — 17.95
- Saudi Arabia — 16.96
- Oman — 16.9
- Australia — 15.22
- Canada — 14.43
- Kazakhstan — 14.22
- United States — 13.68
- Turkmenistan — 13.37
- Luxembourg — 13.24
How Can the Agricultural Sector Minimise Its Greenhouse Gas Emissions?
Reducing agricultural emissions is difficult due to the extensive nature of agriculture and the crucial relevance of agriculture in the lives (and livelihoods) of billions of people. Agriculture employs about two billion people, or 25% of the world’s population, reducing emissions would necessitate all of their efforts and more.However, this goal is not unachievable; agriculture has always provided solutions to humanity’s most pressing issues. The sector has increased food output to levels previously thought to be unachievable.
Now, at a vital juncture in time, the industry has another opportunity to greatly contribute to humanity’s progress. By managing carbon and nitrogen flows in agricultural systems more effectively, greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from agricultural activities can be decreased. Here are a few good management techniques that have been shown to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.

Management of livestock and manure:
The management of manure and livestock are two major sources of agricultural GHG emissions. Practices like the ones listed below can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions from manure and animals by sequestering carbon:
- Use additives in livestock feed
- Technologies that boost livestock production efficiency, such as better animal health monitoring to prevent sickness
- To capture carbon in the soil, use rotational grazing
- Choose feed of a good calibre to lessen methane generated during enteric fermentation
- Manage manure to lessen nitrous oxide and methane emissions
- Manure warehouses with covers
- Nutrient management strategy to maximise the usage of manure
- Manure storage methane should be captured and burned.
Efficient use of on farm equipment and fuel management
There are various options for fuel switching and energy conservation within each farm operation. Several instances include:
- Encouraging the use of zero-emissions farm machinery and equipment
- Improving equipment upkeep
- By replacing the usage of fossil fuels, renewable energy sources can lower GHG emissions both on and off farms
- Improving the fuel efficiency of farm and fishing vehicles
- Conversion of flood irrigation to drip or sprinkler irrigation
Adopt sustainable farm practices
Ecosystems supporting agriculture have significant carbon stocks. The following agricultural methods encourage carbon sequestration by either increasing carbon storage or decreasing carbon storage loss:
- Improved and measured fertilization practices: example in paddy fields Sulphate containing fertilizers (such as Ammonia Sulphate) and Sulphate amendments (such as gypsum) outcompete methane-producing bacteria in fields, can thus reduce 40% the amount of methane released.
- Increase the use of controlled-release and stabilised fertilisers
- minimise tillage
- Reduce barren fallow areas
- Reintroduce crop residue back to the soil
- Investment in cutting-edge technology that promotes sequestration through reforestation, afforestation, and other means
What Is Cropway Doing to Help Reduce Carbon Emissions?
Combating climate change while simultaneously feeding the world will be a difficult task. To meet the Paris agreement’s 1.5°C target, an industry-wide effort and collaboration from consumers, farmers, industrial players, investors, and regulators will be required (or anything near to it). However, improved and sustainable agricultural management techniques, together with contemporary technology, hold a bright future for this goal of lowering net emissions. Cropway will accompany you and your company on this tough journey. Our tools and resources can assist you in calculating how to manage land sustainably, get the most value out of it, and accomplish your environmental and financial goals!
You might also want to read our agricultural blog :- What is the Real Cost for Avocados?