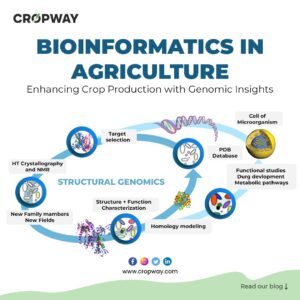
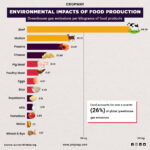
India is known for its various traditional and medicinal crops. Medicines have been in our ancient scriptures for more than 3000 years old. Even in our holy epics such as Ramayana and Mahabharata, there is mention about the various medicinal plants and shrubs. In this blog, we will talk about the medicinal plants named as Ashwagandha.
Why grow Ashwagandha?
Ashwagandha is also known as wonder herbs as it has multiple medicinal properties. It derives its named “Ashwagandha” as its roots smell like horse and it vitalize body. Its seeds root and leaves are used for preparing various drugs. Drugs prepared from Ashwagandha used for stress reliever, to treat senile dysfunction also used to control anxiety, depression, phobia, schizophrenia etc. Rajasthan, Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh are major growing states in India.
SOIL
Ashwagandha gives best result when grown in sandy loam or mild red soil with good drainage having pH in the range of 7.5 to 8.0. Growing Ashwagandha is not possible in soil that retains moisture and remains waterlogged. The soil should be loose, deep and well drained. Black or heavy soils having good drainage are also suitable for ashwagandha cultivation.
LAND PREPARATION
For Ashwagandha plantation, it requires well pulverized and levelled soil. For fine tilth, plough field 2-3 times and ploughing or harrowing should be done before rains and then farm yard manure is applied. Land is prepared in month of April-May in Kharif and in Rabi 0ct.
SOWING
For ashwagandha cultivation prepare nursery in the month of June-July in kharif and in month of Oct-Nov in Rabi.
Seed Rate
For good varieties use seed rate of 7-8 kg per acre.
Manures and fertilizers
The crop does not require heavy doses of manures and fertilizers. It responds well to organic manures and addition of 10 tonnes FYM / 1 tonne vermicompost per hectare is recommended. Application of 15 kg of Nitrogen and 15 kg of Phosphorous per hectare is beneficial for higher production.
Harvest Management
Crop Maturity and Harvesting:-
Harvesting starts from January and continues till March. The plants start flowering and bearing fruits from December onwards.The crop is ready for harvest in January – March i.e. 150 to 180 days after sowing.The maturity of crop is judged by drying out of leaves and yellow red berries. The entire plant is uprooted for roots, which are separated from aerial parts by cutting the stem 1- 2 cm, above the crown. The roots are cut transversely into small pieces (7 to 10 cm). Occasionally, the roots are dried as a whole. The berries are plucked from the dried plants and are threshed to obtain the seeds.
Post-harvest Management:-
The dried roots, entire or transversely cut into smaller pieces, have to be further water washed, cleaned, trimmed and graded. The roots are beaten with a club, which removes adhering soil and breaks off the thin, brittle lateral rootlets. Lateral branches, root crown and stem remains on roots are carefully trimmed with the help of knife.
Grading: The entire product is then carefully sorted into four grades based on the thickness and uniformity of the pieces.
A-Grade: Root pieces up to 7 cm in length, solid, with 1.0-1.5 cm diameter; they should be brittle and pure white on the inside.
B-Grade: Root pieces up to 5 cm in length, solid, with a diameter of less than 1 cm, the roots should be brittle and white on the inside.
C-Grade: Root pieces up to 3-4 cm in length, side branches solid, with a diameter of 1 cm or less.
Lower Grade: Small root pieces, semi-solid, very thin or very thick, chopped and yellowish on the inside..
Yield: On an average yield from one hectare area under commercial cultivation is an approx 0.5- 0.7 tonnes of dried roots and 30- 40 kg seeds.
Therapeutic Uses
- The drug is rejuvenating agent; mainly used in Ayurvedic and Unani preparations.
- The plant has anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, fungicidal, anthelmintic, anti-convulsant, anti-stress, immunomodulatory and anti-pyretic properties.
- It is also used in insomnia, weakness, ulcers and painful swellings as aphrodisiac and in leucoderma.
- The paste prepared out of its leaves is used for curing inflammation of tubercular glands and that of its roots for curing skin diseases, bronchitis, ulcer and dyspepsia and eye diseases.
- The fruits and seeds of Ashwagandha are diuretic in nature.
- The leaves are reported to contain anthelmintic and febrifuge properties.
- An infusion of the bark is given for asthma.
How do farmers benefit by growing it
Aswagandha has tremendous benefits and cultivation of the roots, leaves, plants, and fruits have various economic benefits, such as the demand for this is constantly raising in the domestic and international markets, so have good export potential. Thus people are looking for natural sources such as Ashwagandha for diseases such as depressions and stress. The plant has demand in the cosmetics and pharmaceutical industries. The Ashwagandha plant for weight loss is getting attention in India and all over the world.
Ashwagandha Products
- Ashvagandha – Tablets
- Ashwagandha Peanut Butter
- Ashwagandha Roots
- Ashwagandha Skin Cream
- Ashwagandha Oil
- Ashwagandha Doodh