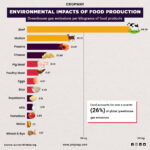
Introduction
The deteriorating quality of air stands as a critical environmental concern and air pollution is one of the greatest threat to health.With a surge in pollutants compromising the air we breathe. Essential to life and ecosystems, air constitutes an integral part of Earth’s atmosphere. Predominantly composed of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), with minor gases like argon and trace elements including carbon dioxide, methane, hydrogen, and helium, making up approximately 1%. Escalating pollution levels pose a significant threat to this inseparable component, demanding urgent attention for the preservation of life and ecological balance.
Common airborne chemicals such as sulfur dioxide, fluorides, and peroxyacyl nitrate pose a significant threat to leaves. Sulfur dioxide induces alterations in leaf tissue color, manifesting as white, yellow, or brown patches. Exposure to these pollutants leads to diminished concentrations of photosynthetic pigments, specifically chlorophyll and carotenoids, impacting plant productivity, seed germination, pedicle length, and inflorescence flower count. Chlorophyll, responsible for absorbing solar energy in the blue and red portions of the electromagnetic spectrum, suffers depletion when environmental pollution exceeds physiological tolerance. This overexposure disrupts photosynthesis, signaling adverse consequences for plant vitality and ecological equilibrium.
The Essence of Chlorophyll
As air pollution emerges as a pressing global issue, the focus has primarily centered on its effects on human health, the environment, and ultimately, food production. Overlooked is the vital role of chlorophyll, the green pigment within plant cells, crucial for photosynthesis. This transformative process harnesses sunlight, converting it into energy, empowering plants to self-generate sustenance. Chlorophyll’s intricate molecular design facilitates sunlight absorption, converting it into vital chemical energy crucial for the growth and sustenance of plant life.


Diminished chlorophyll results in reduced energy production, hindering plant growth. This domino effect weakens individual plants and has cascading repercussions, impacting ecosystems at large.Yet, this fundamental connection is under threat. Widespread air pollution, stemming from industry, agriculture, transportation, and urbanization, introduces significant pollutants such as CO2, CO, SO2, NOx, NO2, and C2H4 through hydrocarbon combustion in motor engines. This precarious balance now faces escalating challenges.
In addition to chlorophyll, the existence of pollutants can lower the average pigmentation rate of photosynthesis, impacting the overall health of plants. In certain instances, it may modify the light spectrum affinity of pigments such as carotenoids, thereby influencing plant responses to environmental cues and potentially causing damage to its physiology.
Defense Mechanisms Plants Use Against Air Pollution
Plants deploy a range of defense mechanisms, including structural adjustments where shifts in bud and flower development patterns may occur as a response to environmental challenges. Physiological defenses involve actions such as closing stomata to minimize pollutant intake, while metabolic strategies aim to counteract stress induced by air pollutants. One such example isProline, a prevalent compatible osmolyte, that plays a crucial role in aiding the plant’s survival during stressful conditions caused by vehicular air pollution. Elevated proline levels can serve as an indicative marker for vehicular pollution.
Visible Signs of Distress
The impact of air pollution on chlorophyll levels manifests in the visible changes to plant health. Stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and premature leaf drop become poignant indicators of a plant grappling with the toxic cocktail in the air. These symptoms, often overlooked in the bustling urban landscape, signal not only the plight of individual plants but also the declining health of our shared ecosystem.
Ecosystem Consequences
Beyond endangering human health, air pollutants inflict harm on food crop yields, compromising nutritional quality and safety, posing a significant threat to food security. The repercussions of declining chlorophyll levels reverberate beyond individual plants. As primary producers falter, herbivores relying on them for sustenance encounter food scarcity. This disruption extends through the food chain, impacting predators and, ultimately, disturbing the balance of the entire ecosystem.
According to a 2014 report, air pollution has slashed wheat and rice yields in India by half. Researchers attribute this primarily to ground-level pollutants. Between 1980 and 2010, yields were up to 36% lower due to air pollution trends. Nature’s delicate balance is disrupted, setting off a chain of ecological consequences. Recent investigations reveal that air pollutants like Sulphur dioxide (SO2), Nitrogen oxides (NOx), and Ozone (O3) severely hamper crop production. The impact isn’t solely dependent on concentration but also on the duration and composition of pollutants. Among these, Ozone emerges as the most phytotoxic element, amplifying the challenges faced by agricultural ecosystems.
Mitigation Strategies to Minimize air Pollution


While complete eradication of air pollution may be elusive, concerted initiatives can maintain it within tolerable limits. To rescue our oxygen-deprived greens, strict regulations on industrial emissions, sustainable transportation promotion, and afforestation efforts are crucial. Embracing innovative technologies like air-purifying plants and green infrastructure can help restore equilibrium between urbanization and nature.
Some of the points to reduce air pollutants:
- Implementing a multifaceted approach: is imperative to combat air pollution and promote environmental sustainability. Research, law enforcement, and public awareness through mass media are essential components of a comprehensive strategy.
- Preventing deforestation is crucial, and greening urban spaces can restore ecological balance. Addressing rural air pollution involves introducing improved cooking stoves. Strict enforcement of air pollution mitigation plans in large construction projects, coupled with import controls on coal quality for industries, is essential.
- Regular inspection and maintenance of steel mills, cement, and glass factories, along with adherence to emissions standards at new plants, contribute to pollution reduction.
- Utilizing eco-friendly construction materials, enforcing vehicle inspections, and banning older vehicles in cities are vital.
- Emphasizing clean energy, promoting walking and cycling, and encouraging hybrid vehicles foster sustainability.
Ultimately, collective efforts are indispensable to create a greener, cleaner environment and mitigate the adverse effects of air pollution.
Conclusion
Air pollutants from industries and automobile emissions are active ecological agents, degrading our environment. In the silent battle for survival, our green allies bear witness to the repercussions of human actions. The profound consequences of air pollution on chlorophyll levels in leaves stand as a poignant reminder of the intricate interdependence of all living entities, highlighting the profound impact our choices have on the delicate balance of the natural world.
The deleterious effects of common airborne chemicals on leaves, manifested in altered tissue color and diminished concentrations of photosynthetic pigments, exemplify the intricate connection between air quality and plant health.Recent studies underscore the direct correlation between environmental stress and plant energy production. A proactive approach is imperative to curtail air deterioration. Effective planning and execution are crucial to halt environmental stress. Controlling air pollution is paramount to preserving the energy production capacity of plants.
Initiatives include enhancing public transportation in urban areas to discourage private vehicle use, ensuring timely road maintenance, and initiating afforestation and landscaping projects in cities. Only through unified endeavors can we aspire to revive the equilibrium between humans and nature, enabling the breathless greens to thrive once more in the symphony of life.