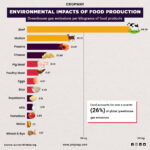
Introduction:
Pollination is crucial for agriculture as it serves as a fundamental pillar for crop production. Plants rely on various vectors like water, wind, and animals (such as bats, moths, hoverflies, birds, bees, butterflies, wasps, thrips, and beetles) to move pollen between flowers. Animal pollinators, especially bees, play a significant role in this process.animal-based pollination is responsible for about 30% of global food production, with bee-pollinated crops alone contributing to approximately one-third of the human dietary supply.
According to bee experts at the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, Approximately one-third of the world’s food production depends on bees and other pollinators. Bees, as crucial pollinators, play a vital role in global food production. They transfer pollen from one flower to another, enabling plants, including essential food crops, to reproduce and produce fruits and seeds.
Importance of Beekeeping in Agriculture

Honeybee pollination services offer remarkable value, 15-20 times greater than all hive products combined. Moreover, the improved pollination quality leads to crop yield boosts ranging from 5% to an astounding 33150%, underscoring the crucial role of bees in enhancing agricultural productivity and food security.
Honey bees, as the 5th input in agriculture, play a crucial role in regulating the efficacy of land, labour, capital, and management inputs. Through pollination, bees significantly enhance crop yields, ensuring the success of seed growth, optimizing fertilizer and pesticide use, and overall, improving agricultural productivity and sustainability.
Beekeeping Industry in India

India has a thriving beekeeping industry, with approximately 12,699 registered Beekeepers and 19.34 lakh honey bee colonies under the National Bee Board. In the year 2021-22, India produced a significant 1,33,200 Metric tonnes of Honey, showcasing its prowess as a major honey-producing nation. Moreover, India’s position as a prominent honey exporter is evident, having exported 74,413 MT of Honey worth Rs. 1221.17 Crores during the same period. Surprisingly, more than 50% of India’s honey production is exported to 83 countries, with the USA, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Bangladesh, and Canada being the major markets for Indian honey, solidifying its global presence.
World scenario of beekeeping

China, USA, Mexico, Argentina, Ukraine, Turkey, Russia, and India are the major honey-producing countries contributing to 90% of the world’s total production. These nations boast rich biodiversity and favorable climatic conditions for extensive beekeeping, enabling them to harvest vast quantities of high-quality honey, thereby dominating the global market.
Bees at Risk: Pesticides and Air Pollution Threaten Pollinators

Bees and other pollinators like butterflies, bats, and hummingbirds face mounting threats from human activities. Global bee populations have been dwindling due to habitat destruction, intensive farming methods, altered weather patterns, and the extensive application of agrochemicals like pesticides. These combined factors jeopardize their vital role in pollination, endangering biodiversity, food security, and ecological balance.Urgent conservation efforts are essential to safeguard these crucial species, as they play a vital role in pollinating crops and sustaining ecosystems, directly impacting food production and biodiversity.
Air pollutants disrupt the natural communication between plants and bees by interfering with scent molecules used by bees to locate food. This interference leads to reduced foraging efficiency, making bees slower and less effective at pollination. Although most pollinators are wild (including more than 20,000 species of bees), mass breeding and large-scale transport of pollinators can introduce risks, facilitating the transmission of pathogens and parasites among populations. Balancing environmental health and sustainable practices is essential to protect these crucial pollinators and ensure the stability of ecosystems and food production.
Conclusion:
The rising demand for food security necessitates the crucial role of bees and other pollinators in crop pollination, benefiting global food supply with fruits, vegetables, oilseeds, and legumes. Bee pollination significantly improves the quality and quantity of cash crops like coffee, cocoa, almonds, and soybeans compared to self-pollination. However, bee colonies face challenges such as climate change, pesticides, land use, and management practices, affecting their growth, reproduction, and sustainability. Recognizing and addressing these factors is essential for ensuring productive and sustainable pollination for the benefit of agriculture and food production.