Postharvest losses are a significant concern in global agriculture
Despite rising global food demand, one-third of all produced food is wasted, with over 40% occurring in postharvest supply chains. This critical issue threatens sustainable food systems. Excessive losses result from subjective quality assessments, inadequate storage, a lack of standardized checks, and poor market linkages. Addressing the issue of food losses holds significant importance in the global efforts to alleviate hunger, boost income, and enhance food security, particularly in the world’s most impoverished nations. The repercussions of food losses extend to the security of food for the underprivileged, the quality and safety of food products, economic development, and the environment.
The specific causes of food losses vary across regions and are closely tied to the unique conditions and circumstances of each country. In a general sense, factors such as crop production choices, internal infrastructure and capabilities, marketing chains, distribution channels, and consumer practices all play a role in influencing food losses. Regardless of a country’s economic development level and system maturity, it is crucial to minimize food losses. These losses signify a squandering of resources invested in production, including land, water, energy, and inputs.
Ninety percent of farmers dry crops in open fields, risking exposure to rodents, birds, and insects. Addressing postharvest grain loss not only safeguards harvests but also presents a virtual land gain, equivalent to three times the cropland area of France, emphasizing the immense potential for agricultural efficiency and sustainability.
Postharvest Losses Interrupt Indian Agriculture

Reducing grain losses is challenging due to varying factors like geographic location, climate, and pest prevalence. Urgent and systemic improvements are essential to reduce post-harvest losses and ensure a more sustainable and efficient food supply chain for the growing global population.
Post-harvest losses pose a significant hurdle for the Indian agricultural sector, with a staggering 30 percent annual loss, as reported by the Ministry of Food Processing Industries. This issue disproportionately affects small-scale farmers.
Understanding the Problem:
Postharvest losses occur when agricultural commodities deteriorate in quantity and quality after harvest. Causes include biological factors, inadequate storage, inefficient transportation, and limited market access. In regions with technological gaps, lack of preservation methods contributes to losses. Economic repercussions impact both small and large-scale farmers, leading to reduced income and increased food prices. Addressing this multifaceted problem requires improved infrastructure, technology dissemination, and better information access. Mitigating post-harvest losses is essential for enhancing food security, sustaining agricultural economies, and fostering a more efficient and resilient global food supply chain.
How to Overcome Postharvest Loss

The traditionally overlooked post-harvest value chain is now embracing innovative, technology-driven solutions, emphasizing a shift towards quality-centric approaches for enhanced efficiency and sustainability in agriculture.
Various approaches & technologies, encompassing both green and digital technologies are on the rise to diminish food waste at the consumer level.This infusion of cutting-edge technologies is revolutionizing the entire agricultural value chain, benefiting all stakeholders. The effectiveness comes from encompassing aspects such as storage, packaging, pre-treatment, portion control, composting, traceability, and aligning supply with demand.
Specifically, during the grain-harvesting stage, technologies like mechanical reapers may prove more effective in minimizing losses, whereas at the grain-drying phase, the greatest impact could be achieved through the implementation of mechanical drying methods. The sustained adoption of these technologies in emerging markets hinges on external factors such as social, economic, and institutional considerations. Revolutionizing conventional systems, frontier technologies—specifically the synergistic blend of AI, IoT, and ML—emerge as a transformative solution. Some examples of how Cropway is utilizing these technologies to reduce post-harvest:
Improving Fresh-Food Transport and Distribution:
- In the realm of fresh-food transport and distribution, addressing inefficiencies and minimizing food waste is a top priority. Cropway employs smart technologies such as logistics optimization, dynamic pricing, auctioning engines, and price predictions to enhance quality control and streamline logistics throughout the supply chain. By doing so, the platform aims to not only boost efficiency but also empower agribusinesses and farmers to establish improved market linkages and ensure fair price determination based on quality.
Efficient Food Disposal with Enhanced Information:
- Cropway introduces modular, innovative measures for the efficient disposal of food, emphasizing enhanced information provision. This includes the implementation of smart labeling technology and the adoption of dynamic pricing. With automatic discounts based on product proximity to expiry dates, customers are incentivized to make purchases, particularly of soon-to-expire items. This approach not only reduces waste but also encourages responsible consumer choices.
Utilizing Digital Technologies in Cropway’s Marketplace:
- Cropway’s marketplace integrates cutting-edge digital technologies, with a focus on Internet of Things (IoT) innovations such as sensors and shelf life optimization. These technologies play a crucial role in optimizing storage efficiency and improving overall supply chain processes. From seed procurement to produce sourcing, Cropway leverages digital data capture and analysis to enhance agricultural practices and ensure a more effective and sustainable agricultural supply chain.
Comprehensive Agricultural Services by Cropway:
- Beyond addressing specific challenges in food distribution, Cropway offers a comprehensive suite of agricultural services. Ranging from providing agricultural inputs and conducting soil tests to offering crop advisory services and financial support, Cropway also offers drones for crop monitoring and disease management to reduce food waste. Additionally, the platform establishes market linkages, ensuring that agricultural outputs find the right markets, contributing to the economic well-being of farmers and stakeholders alike.
Conclusion:
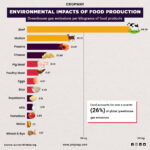
Effective post-harvest management is integral to minimizing losses and optimizing agricultural outcomes. The strategic integration of both traditional and advanced technologies, tailored to specific supply chain stages, is paramount for heightened efficiency, waste reduction, and the promotion of sustainable agricultural practices. Producing food that ultimately goes unconsumed not only results in unnecessary CO2 emissions but also entails the loss of the economic value of the food produced.
In confronting this global challenge, Cropway emerges as a transformative force, utilizing a blend of AI, IoT, and ML technologies. This platform addresses inefficiencies in fresh-food transport and distribution, introduces innovative measures for efficient food disposal, and integrates cutting-edge digital technologies into its marketplace.